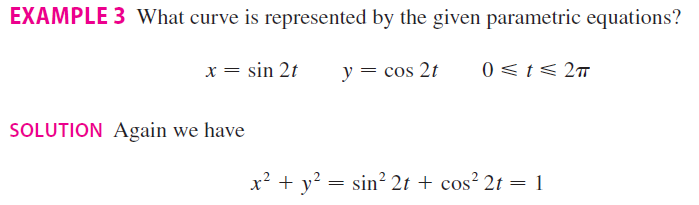Category: math
Conic Sections
Common Parts of Conic Sections
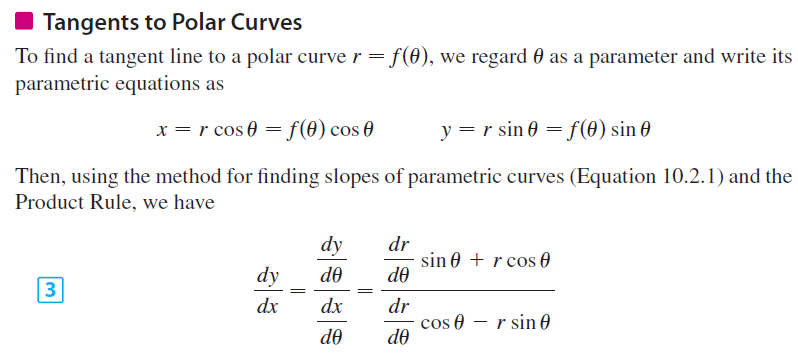
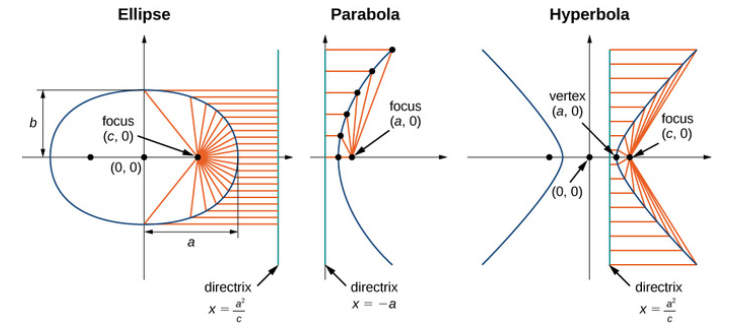
A focus is a point about which the conic section is constructed. In other words, it is a point about which rays reflected from the curve converge. A parabola has one focus about which the shape is constructed; an ellipse and hyperbola have two.
A directrix is a line used to construct and define a conic section. The distance of a directrix from a point on the conic section has a constant ratio to the distance from that point to the focus. As with the focus, a parabola has one directrix, while ellipses and hyperbolas have two.
Eccentricity
- 0 < eccentricity < 1 we get an ellipse,
- eccentricity = 1 a parabola, and
- eccentricity > 1 a hyperbola.
A circle has an eccentricity of zero, so the eccentricity shows us how “un-circular” the curve is. The bigger the eccentricity, the less curved it is.
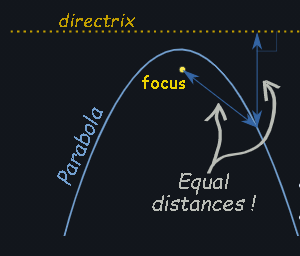
Porabolla
A parabola is a curve where any point is at an equal distance from:
- a fixed point (the focus ), and
- a fixed straight line (the directrix )

Ellipse
“F” is a focus, “G” is a focus,and together they are called foci (pronounced “fo-sigh”).
The total distance from F to P to G stays the same
Well f+g is equal to the length of the major axis.




Hyperbola
A hyperbola is two curves that are like infinite bows.
Looking at just one of the curves:
any point P is closer to F than to G by some constant amount
The other curve is a mirror image, and is closer to G than to F.

- an axis of symmetry (that goes through each focus)
- two vertices (where each curve makes its sharpest turn)
- the distance between the vertices (2a on the diagram) is the constant difference between the lengths PF and PG
- two asymptotes which are not part of the hyperbola but show where the curve would go if continued indefinitely in each of the four directions


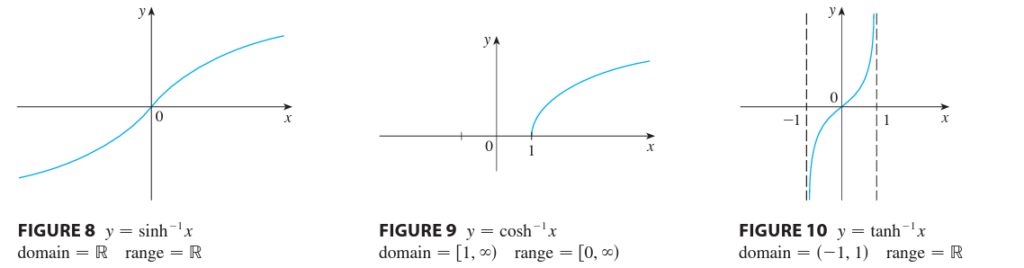
Hyperbolic functions



Catenary (hanging cable)
Math Problems 1
Problem 1
what is the area of the rectangle?
the minimum area of the triangle satisfied these conditions?
part 1

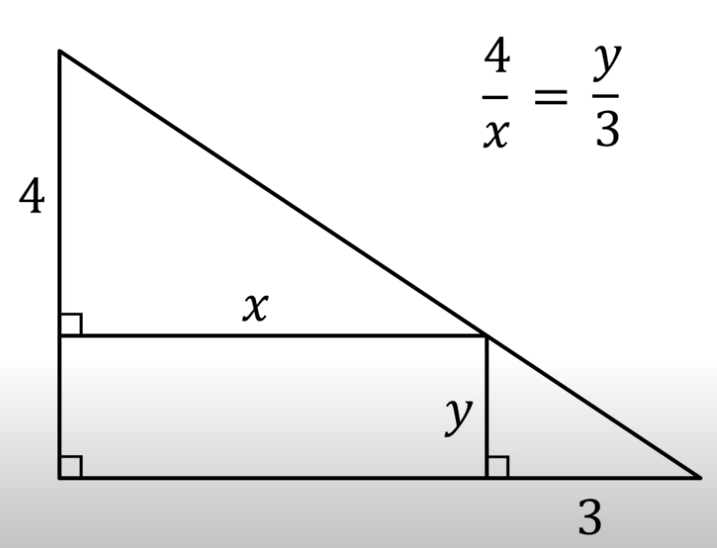
so the area of a rectangle is
xy=12part 2
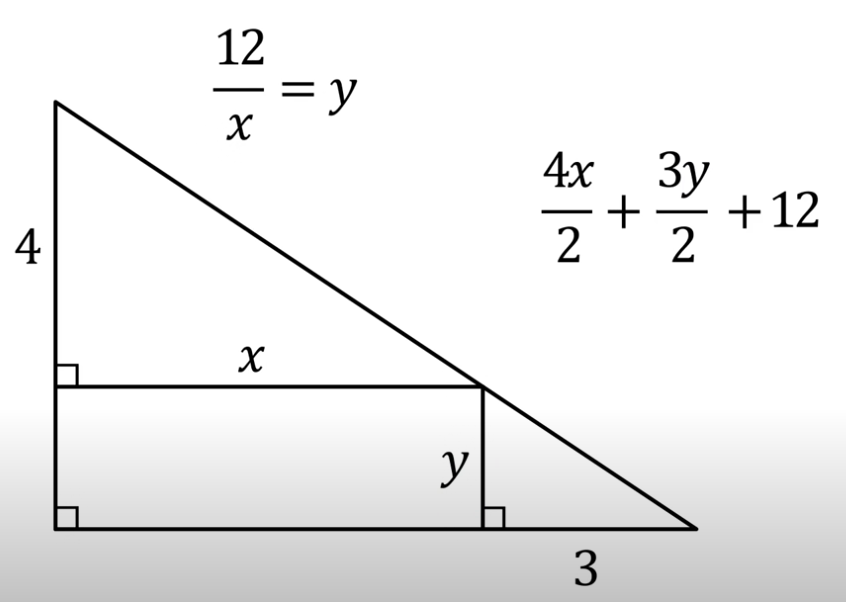

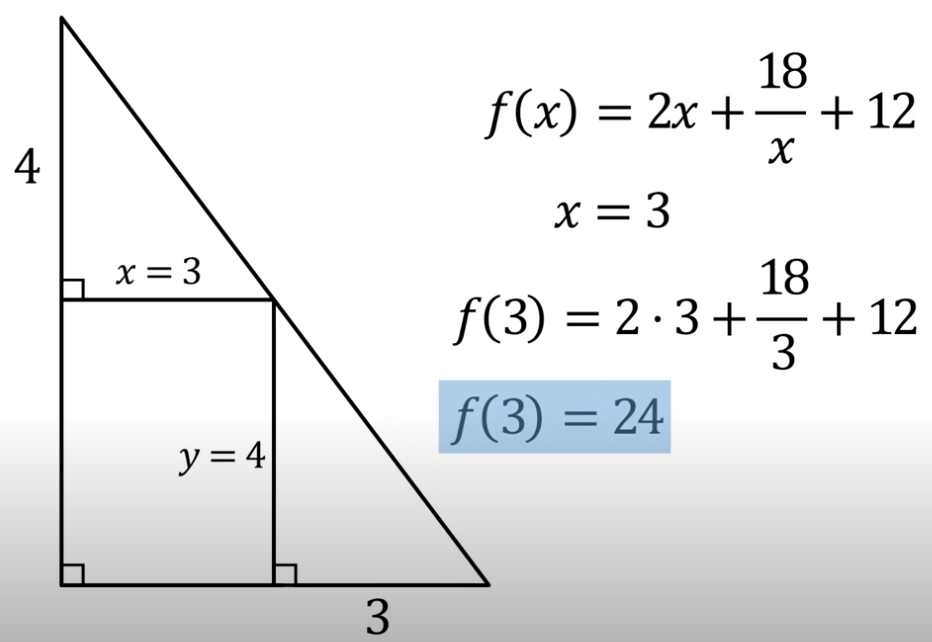
Problem 2
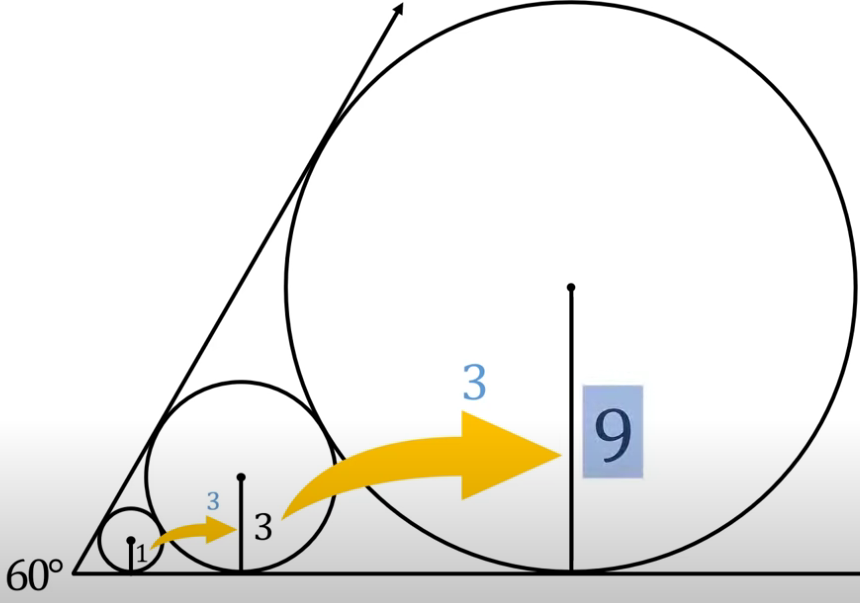
find the radius of biggest circuit
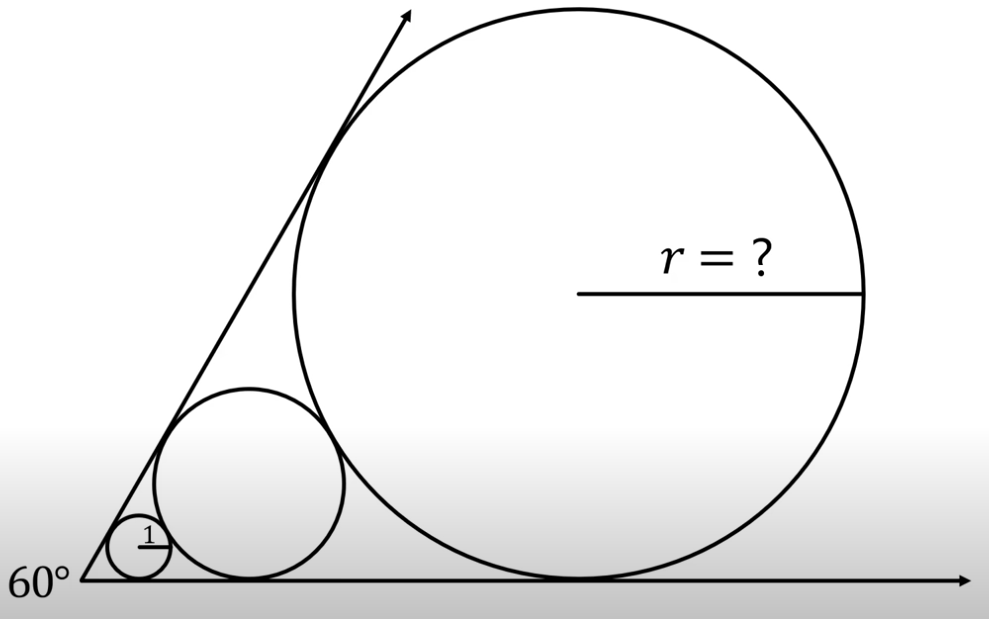
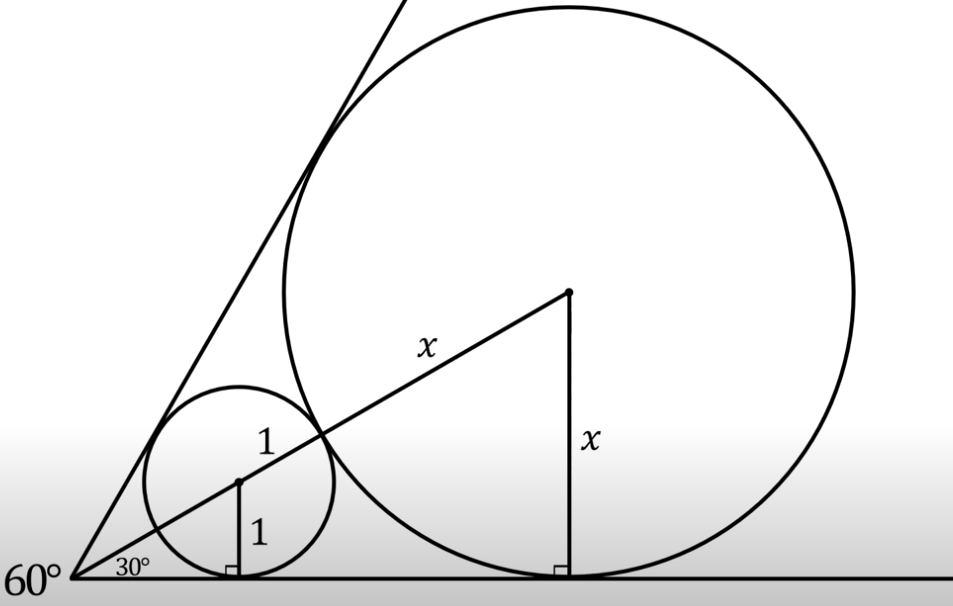
take first two circuits
hypotenuse of both are collinear

Problem 3
a cable of 80 meters hanging from the top of two poles there are two 50 meters from the ground
what is the distance from two poles if center of cable 20 meters above the ground ?



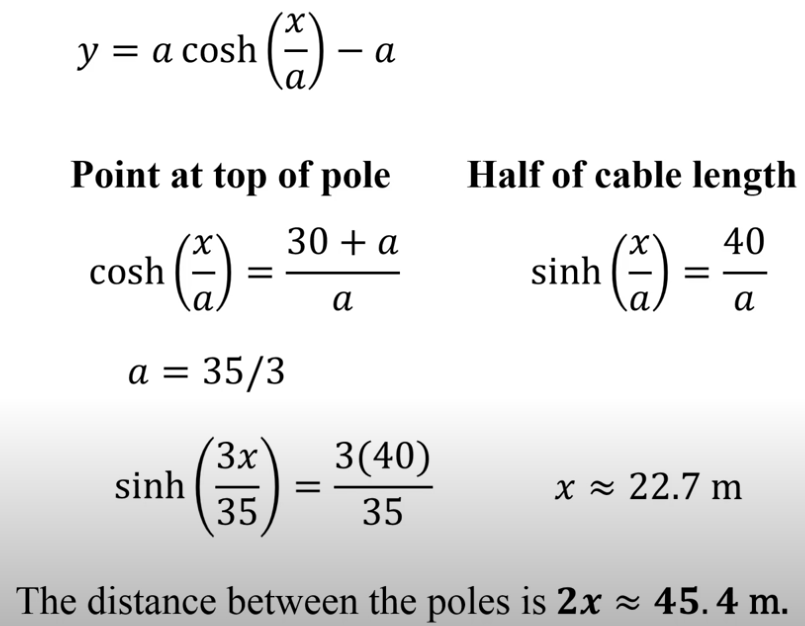
Problem 4
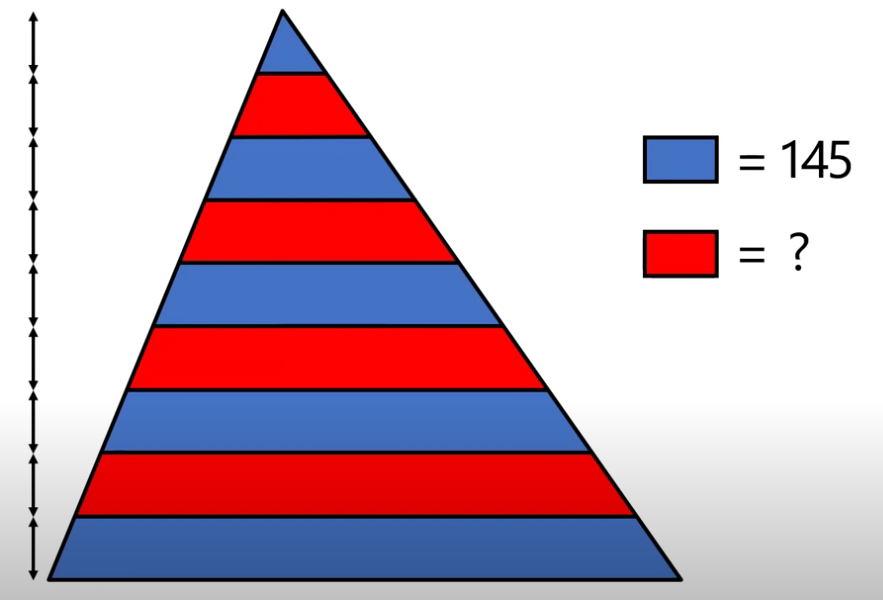
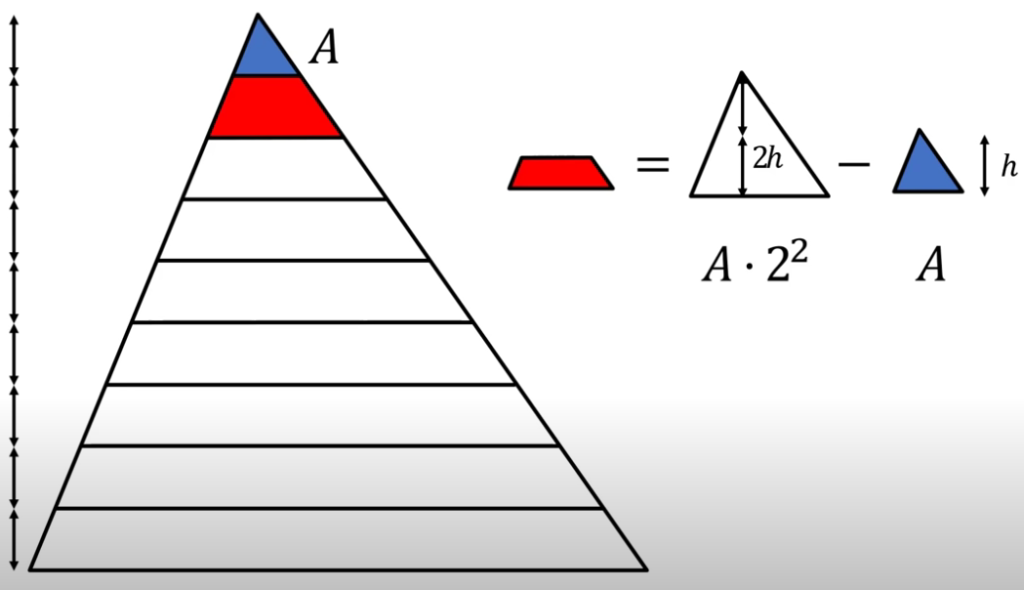
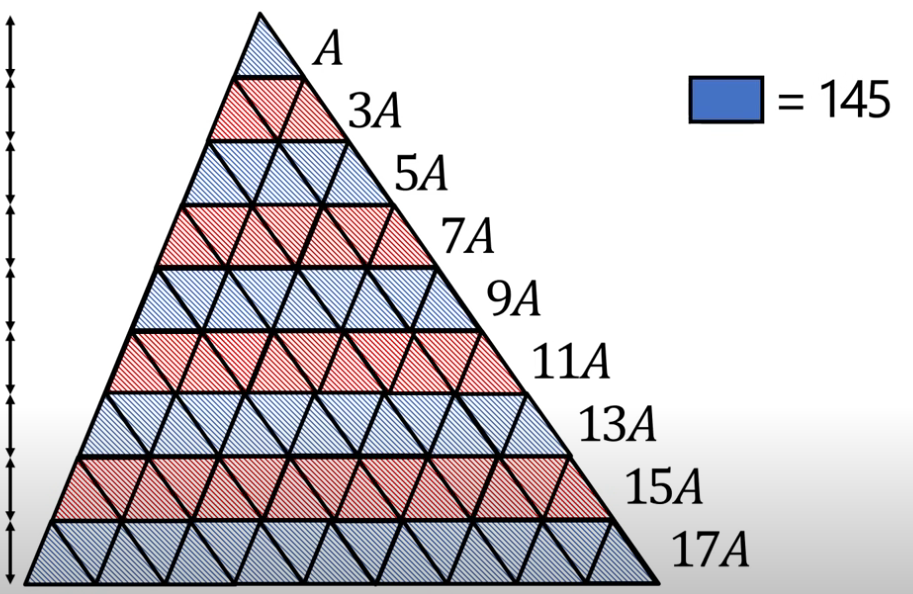
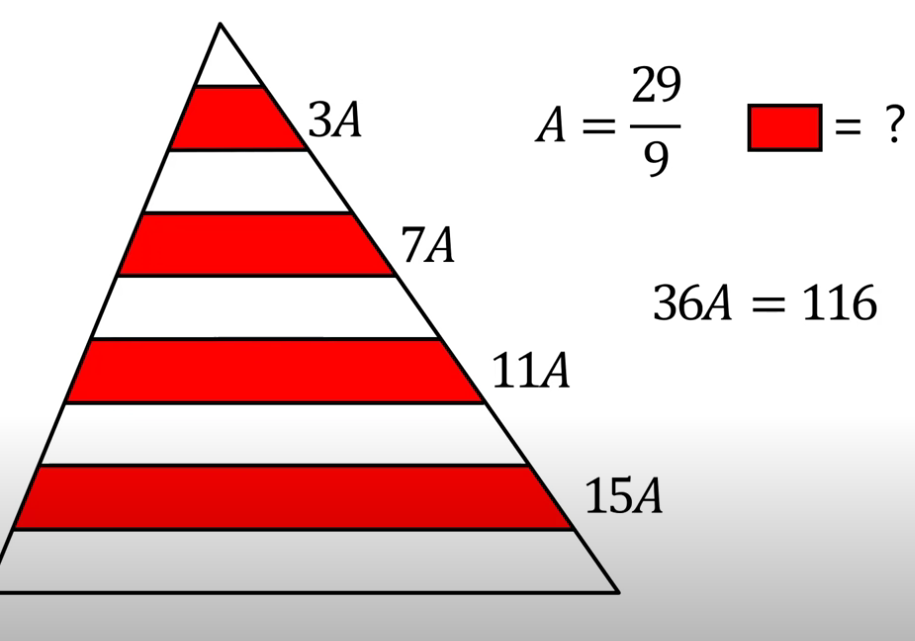
find the area of the red segments
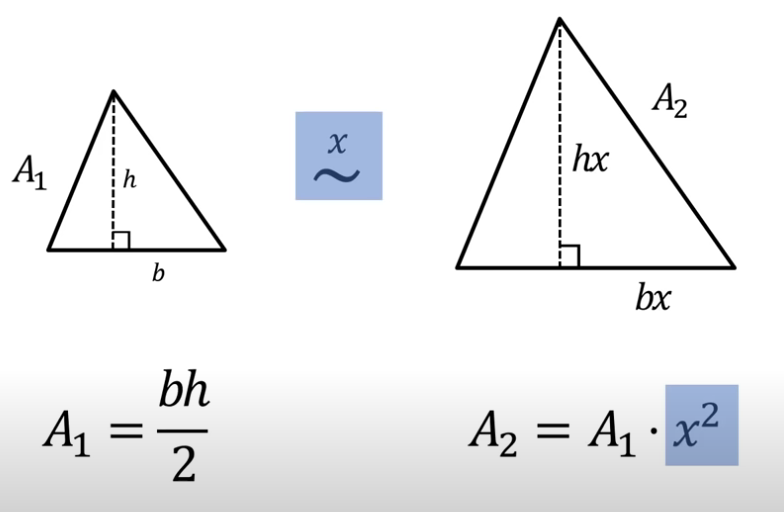
Rotation Transform
basic 2D Rotation



Rotation About an Arbitrary Axis


Homogeneous Coordinates

Four-Dimensional Transforms


Transforming Normal Vectors

Quaternion Mathematics



rotation with quaternion



Spherical Linear Interpolation


Techniques of Integration
Integration By Parts





Trigonometric Integrals










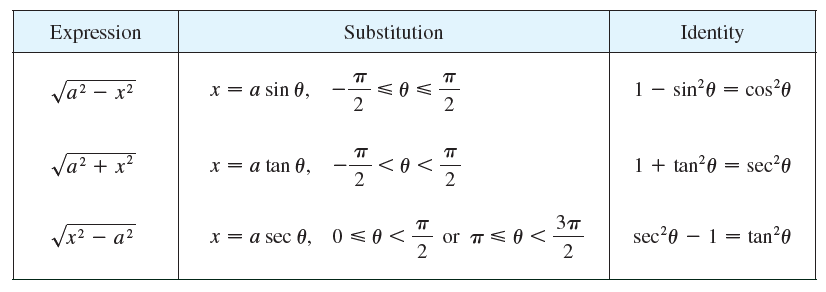
Trigonometric Substitution





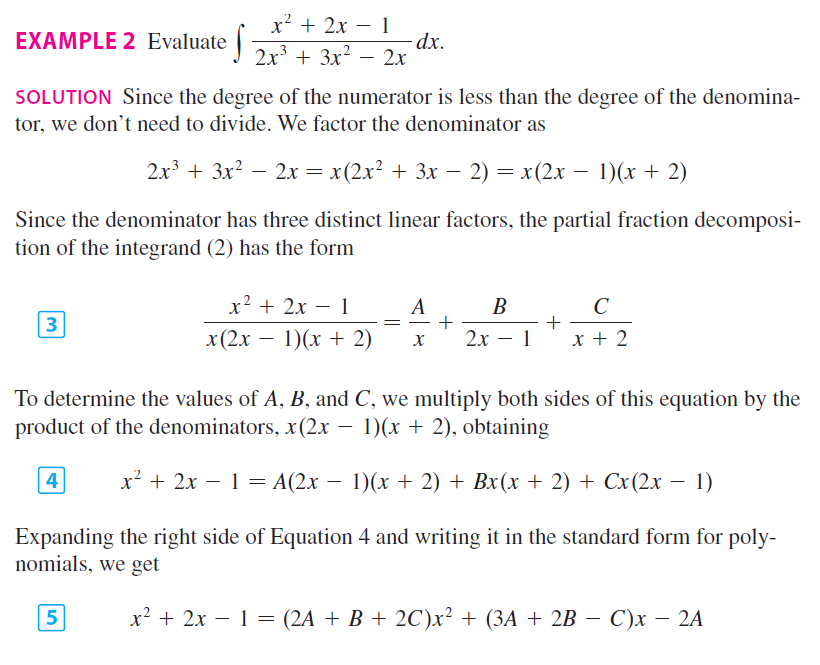
Partial Fractions








Strategies For Integrations



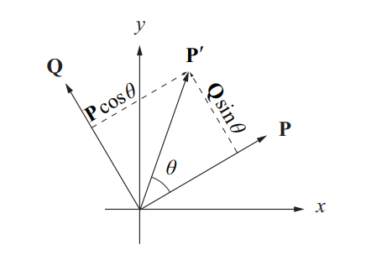
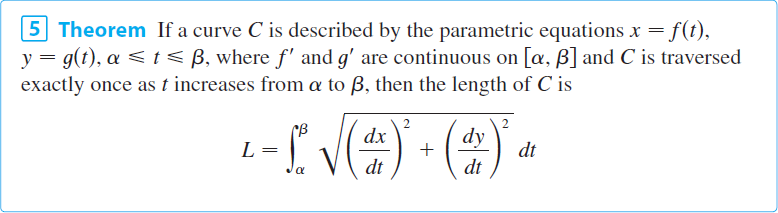
Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates
Parametric Coordinates




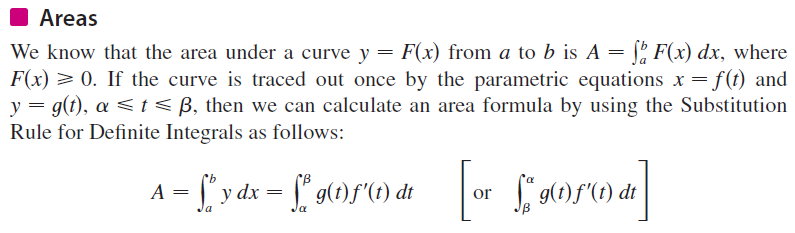

Polar Coordinates